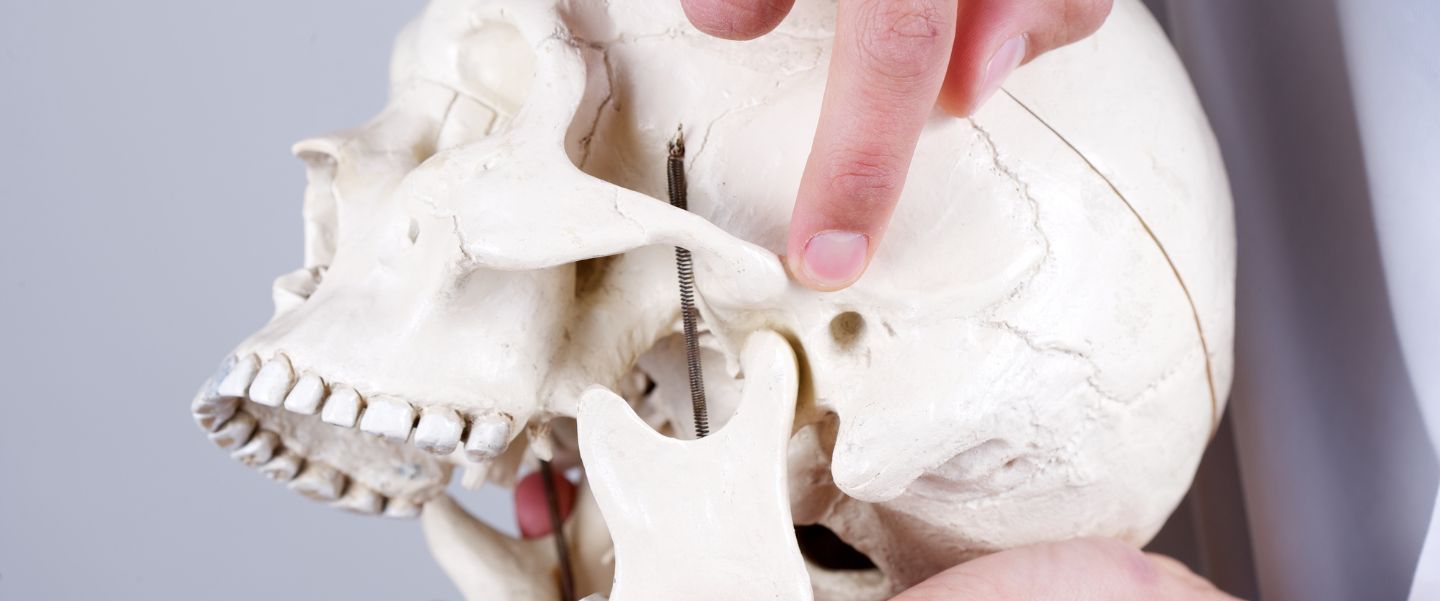
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) refers to the joint near the ear, on both sides of the face, which connects the temporal bone and the mandible.
This joint is made up of bones and ligamentous, muscular, fascial and meniscus structures. The TMJ is therefore responsible for jaw movements, such as eating, speaking and chewing. Although it is a small joint, its importance for the functioning of the body is crucial.
Approximately 5% to 12% of the world’s population suffers from TMJ dysfunction, and this problem is twice as prevalent in women.
What are the most common causes of Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction?
It’s not always possible to determine the origin of this type of dysfunction. However, there are risk factors that can increase the risk of developing this type of problem, such as:
- Trauma to the jaw;
- Diseases such as arthritis, arthrosis or TMJ infection;
- Poor posture;
- Anatomical features related to the formation of the jaw during birth;
- Sleep disorders;
- Difficulty sleeping;
- Stress, depression and anxiety;
- Grinding or clenching of teeth during sleep;
- Bruxism.
What are the symptoms most associated with Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction?
The symptoms that can indicate that someone is suffering from this dysfunction are made up of various symptoms and signs, such as:
- Joint noises (clicking/crying when opening and/or closing the mouth);
- Pain and/or difficulty with movements such as opening and/or closing the mouth.
- Pain similar to earache;
- Pain in the neck/cervical area and shoulders;
- Headaches/headaches;
- Bruxism: involuntary clenching and grinding of the teeth, exerting excessive force on the masticatory muscles, causing the teeth to wear down;
- Tiredness in the face, especially when chewing;
- Change in the fit of the jaw;
- Tinnitus and vertigo.
How is Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction diagnosed?
In order to make a medical diagnosis of this problem, it is first important to carry out a physical examination, in which the muscles and temporomandibular joint are palpated, opening and closing movements are assessed, as well as analyzing joint noises and the condition of the oral cavity (dental health, periodontal health, missing teeth, replacement of missing teeth).
In addition, diagnostic aids such as X-rays, CT scans and MRIs can be used, taking into account the characteristics of each patient.
What are the possible consequences of Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction?
If you think you may be suffering from TMJ dysfunction, you should seek specialist help and start doing TMJ physiotherapy in order to avoid major complications such as degenerative and inflammatory changes.
If this type of dysfunction is left untreated, it can have various long-term consequences, such as:
- Changing the position of the bite and the fit of the teeth;
- Causing pain in other areas of the body;
- Causing changes in body posture.
What are the advantages of treating Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction?
There are many benefits that patients can reap from treating this health problem, including:
- Eliminating and avoiding situations of acute and chronic pain, caused by this type of dysfunction;
- Eliminating and avoiding pain in other areas of the body (such as the neck, ears, spine and head) caused by this dysfunction;
- Improve quality of life by eliminating pain from basic everyday tasks such as chewing, laughing or yawning;
- Avoid dysfunctions in the bite and fit of the teeth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Generally, TMJ physiotherapy is associated with dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), i.e. the malfunction of this joint, damaging the surrounding structures and causing orofacial pain.
Thus, discomfort in the face, TMJ and chewing muscles is usually the main reason why people seek medical help and TMJ physiotherapy.
Yes, here are some examples.
Exercise 1: Relaxing the jaw
- Rest your tongue at the top of your mouth, behind your upper front teeth.
- Let your teeth separate while you relax your jaw muscles.
Exercise 2: Partial opening of the mouth
- Place your tongue on the roof of your mouth and put one finger in front of your ear.
- Now place your middle or index finger on your chin.
- Release your jaw halfway and then close it, without causing pain.
Exercise 3: Opening your mouth wide
- Keep your tongue on the roof of your mouth and place one finger on your TMJ and the other on your chin.
- Release your jaw completely and repeat the step.
Exercise 4: Chin tuck
- Put your shoulders back and your chest up.
- Pull your chin back, creating a “double chin”.
- Hold for 3 seconds and repeat 10 times.
Exercise 5: Mouth opening with resistance
- Place your thumb under your chin.
- Open your mouth slowly, slowly pushing your chin so that it resists.
- Hold for 3 to 6 seconds.
- Close your mouth slowly.
In order to be more effective and show more successful results, ATM physiotherapists often work together with other specialists, such as dentists, maxillofacial surgeons, psychologists, speech therapists and other health professionals.
To avoid major complications, this dysfunction should be treated as soon as possible, not least to prevent it from becoming chronic and starting to affect the patient’s quality of life.
In addition to the use of medication, relaxation drops or other treatments and postural reprogramming, TMJ physiotherapy is recommended in order to resolve this health problem more quickly and effectively.
Only in the most serious cases is it necessary to opt for orthognathic or temporomandibular joint surgery.
Anyone suffering from a temporomandibular joint dysfunction can benefit from TMJ physiotherapy, regardless of whether they are an adult or a child.
Yes, there are some measures you can take to avoid problems with this joint, or at least to ease the pain and discomfort. Here are some of the behaviors to adopt:
- Reduce stress levels in order to prevent bruxism;
- Avoid eating foods that require excessive chewing, such as chewing gum, candy and toffee;
- Avoid eating hard foods such as nuts, whole fruit and pieces of ice.
BOOK YOUR APPOINTMENT ONLINE
We reply within a maximum of 24 working hours.