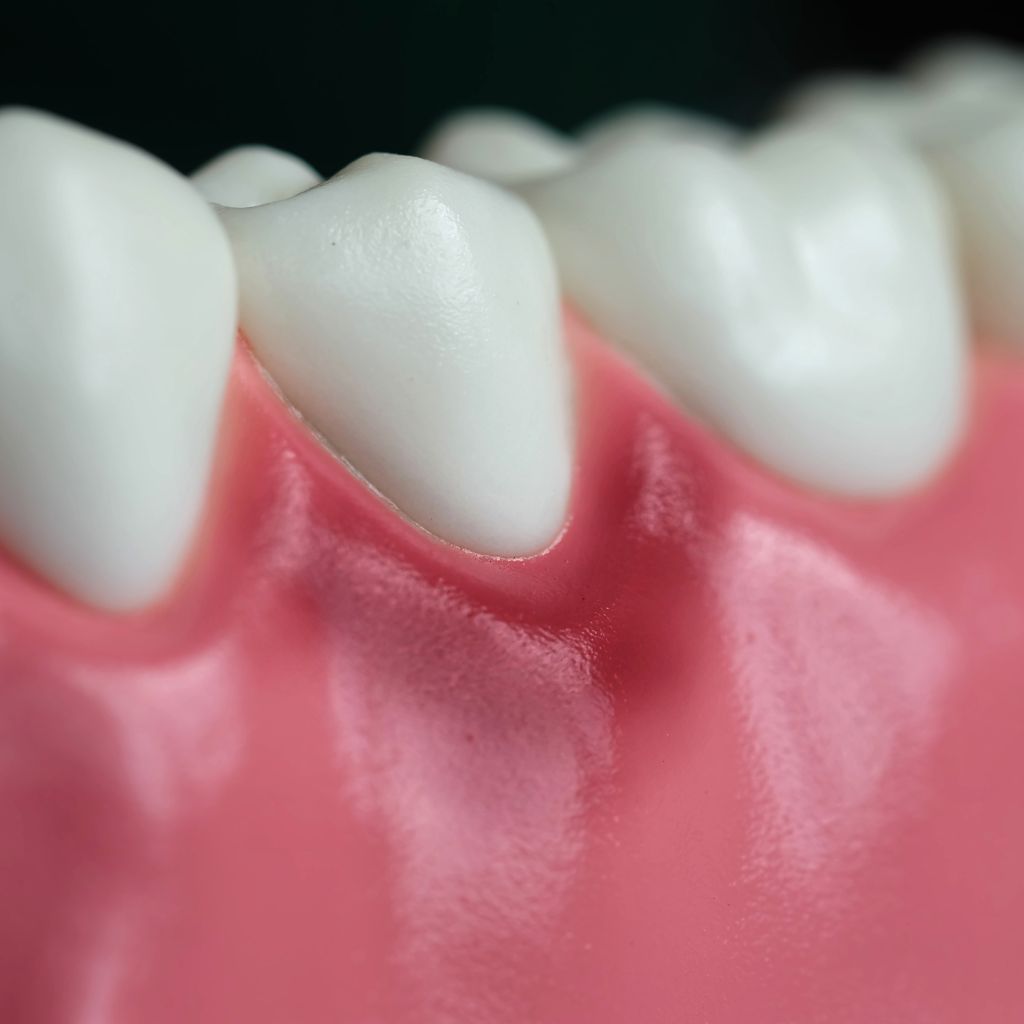
Periodontology is the specialty of dental medicine that deals with the study, diagnosis and treatment of the tissues that support the teeth, specifically the gums and bone. More than half of adults suffer from periodontal disease, which is usually diagnosed late, when symptoms start to appear. This is another reason why regular visits to the dentist are so important. Periodontal disease is a chronic condition characterized by the formation of periodontal pockets between the gum and the tooth, as a result of the accumulation of bacterial plaque. As a result, there can be loss of bone supporting the teeth, tooth mobility, movement and the appearance of gaps between teeth, periodontal abscesses, periodontal pockets and gingival recessions, among other complications. Plaque is an aggregate of bacteria that naturally exists in the mouth and adheres to the surface of the teeth, along with food debris and toxins. If not removed through good oral hygiene habits, plaque becomes harmful, causing periodontal disease. As a rule, bacterial plaque is the cause of periodontal disease. There are also other aggravating factors, such as genetic factors, medication, hormonal changes, smoking and uncontrolled diabetes. This disease is usually an “evolution” of gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums, also caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar around the teeth. If gingivitis is left untreated, it can develop into periodontitis, increasing the risk of bone and gum loss, which jeopardizes the support of the teeth. Peri-implantitis is a disease related to dental implants and affects around 80% of patients. The main characteristic of this disease is the inflammation of the tissues around osseointegrated dental implants. Therefore, when there is bleeding and inflammation of the gums in the implant area, bad breath, pain, swelling, among other warning signs, it is important to consult a dentist and start treatment. The accumulation of bacterial plaque is usually at the root of this disease, which manifests itself after the infection has started. If it progresses, it can even reach the supporting structures of the teeth. Some symptoms of this pathology are the appearance of pus-filled pockets, discomfort and pain in the gums and/or teeth, swelling of the jaw, inflammation of the gums, bad breath and tooth sensitivity. Although it doesn’t usually cause pain, this is a problem that often affects the patient’s self-esteem. Hereditary factors, ethnicity, certain medications or other diseases such as periodontitis or gingivitis can be at the root of this condition. Gum recession is characterized by the tissue moving away from the teeth, leaving them more exposed. In more complex cases, this problem can damage the very structure of the bone. Among the causes of this problem are: bruxism, poor oral hygiene, smoking habits, misaligned teeth, among others. The main symptoms of periodontal disease are: Treatment can vary from patient to patient. However, the aim is always the same: to eliminate the bacteria causing the disease. In the case of gingivitis, the recommended treatment may be to improve oral hygiene and/or carry out a prophylaxis/cleaning treatment, which is fairly simple and quick. If you’re already suffering from periodontitis, you’ll need prophylactic treatment, but you’ll also need to remove the tartar in the periodontal pocket by scraping and root planing the active pockets. There are also situations in which corrective periodontal surgery may be necessary (eliminating periodontal pockets and/or regenerating lost supporting tissues). At the end of this phase, we move on to a maintenance period, the aim of which is to keep the disease completely under control. We reply within a maximum of 24 working hours. Periodontology
What is periodontal disease?
What is plaque and how does it form?
How does periodontal disease develop?
Apart from gingivitis and periodontitis, what other periodontal diseases are there?
Peri-implantitis
Gingival abscess
Dark gums
Gingival recession
What are the main symptoms of periodontal disease?
What treatments are indicated for periodontal disease?
Frequently Asked Questions
BOOK YOUR APPOINTMENT ONLINE
Contact us